 Developmental Neurotoxicity (DNT)
Developmental Neurotoxicity (DNT)
ZeClinics DNT service is a rapid and biologically relevant in vivo screening approach for the prediction of the impact of drug or chemical exposure on the developing nervous system. It relies on complex behavioral evaluations, which provide an accurate understanding of Central Nervous System (CNS) functionality.
It is primarily designed to support the agrochemical industry in the health risk assessment of chemicals, but it can also help early drug development and selection/optimization.
Current OECD guidelines for DNT assessment (426 & 443) are very long, expensive, and have unknown human relevance. As a proof of our commitment to improving toxicity assessment approaches, ZeClinics is participating, as a member of the OECD Expert Group on Developmental Neurotoxicity, in an international initiative to develop DNT Integrated Approaches to Testing and Assessment (IATA). The aim of the project is to draft a new guidance document to provide a DNT in vitro battery (DNT-IVB) that could be used immediately for the screening of all chemicals.
Neurobehavioral tests currently represent one of the most powerful tools to estimate the potential functional and morphological effects of chemicals on the developing nervous system. In this context, the zebrafish expert group has demonstrated the added value of the gold standard zebrafish light/dark transition behavioral assay inside the DNT-IVB. We provide this well-validated assay as a service for DNT assessment to our clients.
Advantages
High experimental throughput for chemical/drug DNT assessment in vivo.
High conservation in development and function between the human and zebrafish brain.
Convenient drug delivery.
Cost-efficiency.
Alternative experimental method to reduce animal testing while evaluating toxicity in vivo.
Method description
Early-life zebrafish embryos are incubated with several concentrations of the compound of interest based on the previously determined Bench Mark Dose (BMD). Different locomotion parameters are assessed in treated larvae at 120 hours post fertilization (hpf) by Light/Dark Transition Test using the Daniovision™ device together with the Ethovision XT software (Noldus IT). Behavioral alterations are subsequently associated with specific drug-induced defects in CNS development.
Readouts
Locomotion activity:
- Total distance moved under light/dark conditions and symptomatic movement patterns
- Distance moved per minute
- Velocity
- Acceleration
- Timing and area of movement
 Figure 1. Larvae videotracking of locomotion activity acquired by Noldus automatic tracking system. Red lines show larval movements.
Figure 1. Larvae videotracking of locomotion activity acquired by Noldus automatic tracking system. Red lines show larval movements.
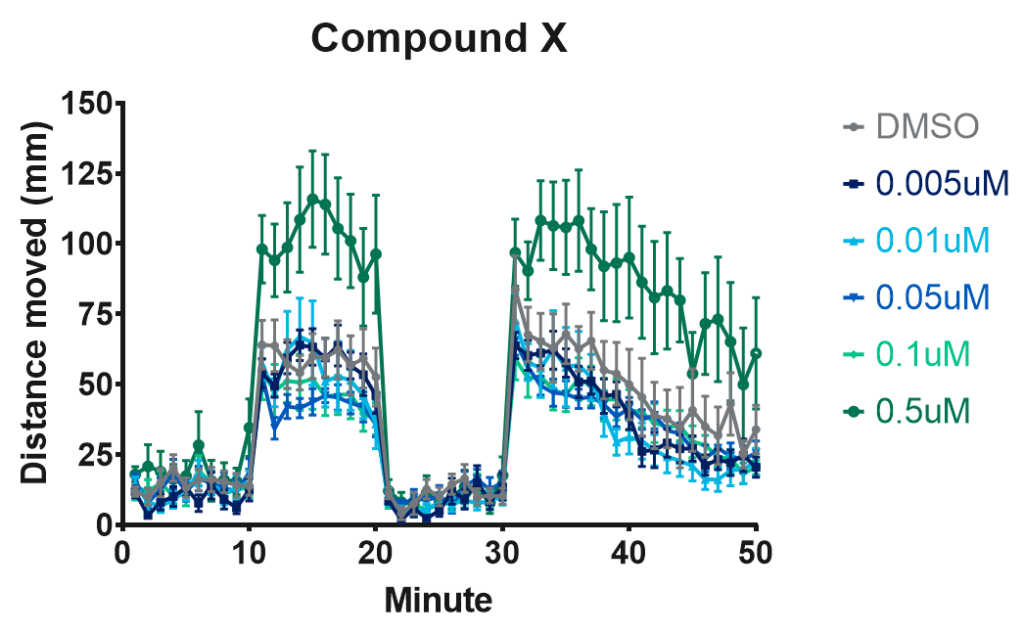 Figure 2. Representative plot of locomotion response to light/dark stimulus of 96 larvae at 120 hpf treated with 7 concentrations of a compound of interest. The higher concentration (0.5uM) of compound X induces hypermobility.
Figure 2. Representative plot of locomotion response to light/dark stimulus of 96 larvae at 120 hpf treated with 7 concentrations of a compound of interest. The higher concentration (0.5uM) of compound X induces hypermobility.
We'd like to hear from you
If you want more information about our NeuroTox
assay or have any other questions, please
contact our experts.
References
- Romero-Ayuso D. Future Challenges in Research in Children with Neurodevelopmental Disorders. Children (Basel). 2021 Apr 23;8(5):328.