 ZeGlobalTox – 3 Analysis Into a 1 Procedure
ZeGlobalTox – 3 Analysis Into a 1 Procedure
ZeGlobalTox is a novel experimental procedure that integrates the analysis of cardio-, neuro-, and hepatotoxicity into a single procedure. The three sequential assays are performed in the same larvae, allowing the reduction of zebrafish used compared to parallel assessments, and streamlining the experimental pipeline. In addition, the high predictivity of ZeGlobalTox allows reducing the use of mammals for organ-toxicity screening in later research stages.
Advantages
Simultaneous assessment of NeuroTox, CardioTox and HepatoTox.
High predictivity referred to humans: 89% specificity, 68% sensitivity and 78% accuracy.
Animal testing and drug volumes reducement.
Method description
A zebrafish transgenic line expressing green fluorescent protein (GFP) in cardiomyocytes is used to determine cardiotoxicity, neurotoxicity, and hepatotoxicity sequentially. We offer a basic and an extended protocol to evaluate neurotoxicity or CNS side effects upon long (24h) and acute (3h) exposure to potentially toxic compounds, respectively.
 Figure 1. Comparison of toxic exposure times (blue bands) and toxicity evaluation timepoints (orange lines) of basic and extended protocols.
Figure 1. Comparison of toxic exposure times (blue bands) and toxicity evaluation timepoints (orange lines) of basic and extended protocols.
Readouts
- Neurotoxicity
- Changes in the basal locomotor activity
- Altered response to light stimuli
- Thigmotaxis (optional in the extended protocol)
- Habituation (optional in the extended protocol)
- Seizures (optional in the extended protocol)
- Cardiotoxicity
- Heartbeat frequency (ventricle and atrium)
- Arrhythmias
- Ejection fraction
- QT prolongation
- Heart chamber (Atrium/Ventricle) diameter
- Hepatotoxicity
- Liver necrosis (boolean)
- Hepatomegaly (estimated liver area)
- Hepatic steatosis: fat accumulation in the liver
 Figure 2. Larval videotracking of basal locomotion activity acquired by NOLDUS system. Red lines show larval movements.
Figure 2. Larval videotracking of basal locomotion activity acquired by NOLDUS system. Red lines show larval movements.
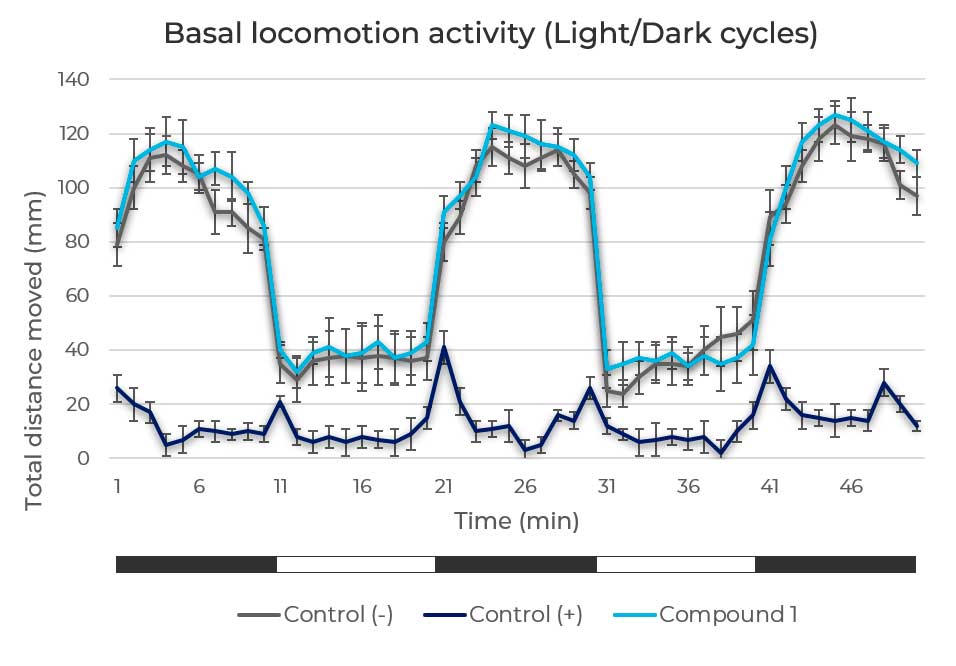 Figure 3. General motor activity assessment. Light/Dark locomotion pattern of zebrafish larvae in response to a negative control, to a neurotoxic compound (positive control) and a study compound that doesn’t produce neurotoxic effect on basal locomotor activity.
Figure 3. General motor activity assessment. Light/Dark locomotion pattern of zebrafish larvae in response to a negative control, to a neurotoxic compound (positive control) and a study compound that doesn’t produce neurotoxic effect on basal locomotor activity.
 Figure 4. Heart tomography of 3dfp transgenic zebrafish larva labelling cardiomyocytes with GFP.
Figure 4. Heart tomography of 3dfp transgenic zebrafish larva labelling cardiomyocytes with GFP.
 Figure 5. Evaluation of hepatic steatosis. (A) Proportion of zebrafish larvae that show increased liver fat after treatment with a candidate molecule compared to negative and positive controls. (B) Representative images of healthy zebrafish larva (image on the left) and steatotic zebrafish livers (middle and right images) after specific fat staining.
Figure 5. Evaluation of hepatic steatosis. (A) Proportion of zebrafish larvae that show increased liver fat after treatment with a candidate molecule compared to negative and positive controls. (B) Representative images of healthy zebrafish larva (image on the left) and steatotic zebrafish livers (middle and right images) after specific fat staining.
We'd like to hear from you
If you want more information about our ZeGlobalTox
assay or have any other questions, please
contact our experts.
References
- Cornet C, Calzolari S, Miñana-Prieto R, Dyballa S, van Doornmalen E, Rutjes H, Savy T, D'Amico D, Terriente J. ZeGlobalTox: An Innovative Approach to Address Organ Drug Toxicity Using Zebrafish. Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Apr 19;18(4):864.